Multivariate Component Tree
The component trees have been extended for multivariate images [Car19]. Right now, only the multivariate tree of shapes [Car15] (MToS) has been implemented in Pylene.
Include
<mln/morpho/mtos.hpp>
-
auto mtos(image2d<rgb8> ima, point2d pstart);
Compute the multivariate tree of shapes and returns a pair (tree, node_map). See Component Trees (Overview) for more information about the representation of tree.
- Parameters:
ima – The input image in RGB format.
pstart – The rooting point
- Returns:
A tree of type
component_tree<void>(no values are related to the nodes of the tree since they do not have a natural value) and a map from image point to node tree.
Notes
Before computing the MToS, the user should add a border to the image, with the values of this border set to the median value of the border of the original image.
The resulting nodemap has a domain size of
4d - 3withdthe input image domain.The MToS not having values related to the nodes, the user has to compute a value for each node, such as the mean of each node (as shown below in example with the
mean_node_accuaccumulator).
Example
This example computes a grain filter, which removes all the node having an area inferior to 100.
#include <mln/accu/accumulators/count.hpp> #include <mln/core/extension/padding.hpp> #include <mln/core/image/ndimage.hpp> #include <mln/morpho/mtos.hpp> #include <mln/io/imread.hpp> // Function to reduce the nodemap to the original image domain mln::image2d<int> reduce_nodemap(mln::image2d<int> n); // Function to get the median of the border values mln::rgb8 get_median_on_border(mln::image2d<mln::rgb8> ima); int main(void) { mln::image2d<mln::rgb8> ima; mln::io::imread("lena.ppm", ima); // Adding a border const auto median = get_median_on_border(ima); ima.inflate_domain(1); constexpr int borders[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 1}}; mln::pad(ima, mln::PAD_CONSTANT, borders, median); // Compute the MToS auto [t, nm] = mln::morpho::mtos(to_process, {-1, -1}); // The rooting point is in the added border // Reduce the nodemap nm = reduce_nodemap(nm); // Remove the border ima.inflate_domain(-1); nm.inflate_domain(-1); // Compute the area of each node of the tree auto area = t.compute_attribute_on_points(nm, mln::accu::accumulators::count<int>()); // Perform a grain filter on the tree t.filter(mln::morpho::CT_FILTER_DIRECT, nm, [&area](int n) { return area[n] >= 100; }); // Compute the mean of the connected component of each nodes auto mean = t.compute_attribute_on_values(nm, ima, mln::accu::features::mean<>(), false); // Reconstruct the tree auto rec = t.reconstruct_from(nm, ranges::make_span(mean.data(), mean.size())); return 0; }
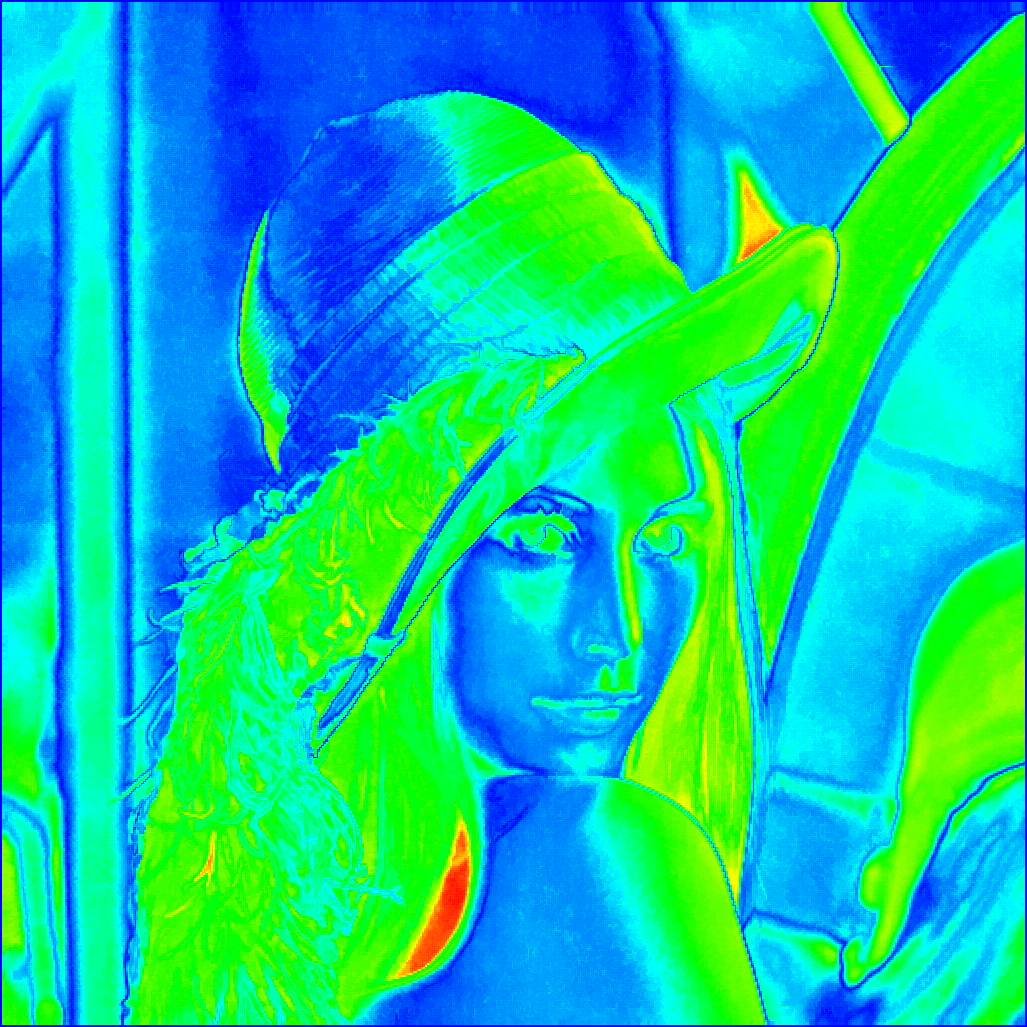
|
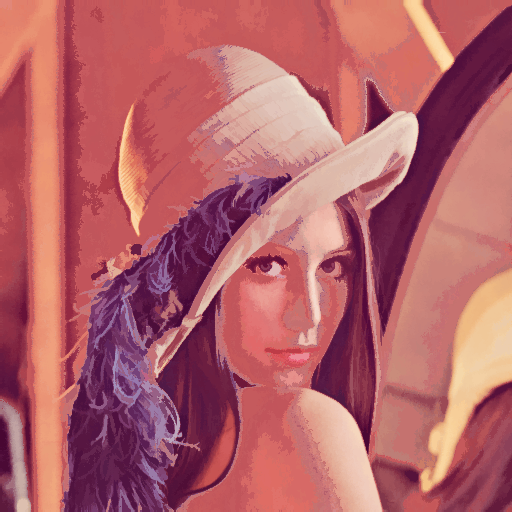

|
The depth map resulting of the fusion of the trees (see [Car15] for more details) |
The reconstructed image from the filtered tree |
References
Edwin Carlinet and Thierry Géraud (2019). Introducing Multivariate Connected Openings and Closings. International Symposium on Mathematical Morphology and Its Applications to Signal and Image Processing. Springer, Cham. 215-227