Opening & Closing by reconstruction
Include <mln/morpho/reconstruction.hpp>
-
template<Image I1, Image I2>
image_concrete_t<I1> opening_by_reconstruction(I1 f, I2 markers, Neighborhood nbh, Compare cmp) -
template<Image I1, Image I2>
image_concrete_t<I1> opening_by_reconstruction(I1 f, I2 markers, Neighborhood nbh) -
template<Image I1, Image I2>
image_concrete_t<I1> closing_by_reconstruction(I1 f, I2 markers, Neighborhood nbh) The opening by reconstruction performs the reconstruction of the image
markersunder the constrain imagef. The markers designate the parts of the image we want to retain. In binary, it is equivalent to perform the conditional dilation of themarkers\(X\), by a structuring element 𝑩, using the reference 𝑓 until reaching stability.\[\delta^{n+1}_{f,\mathcal{B}}(X) = \delta_\mathcal{B}(\delta^{n}_{f,\mathcal{B}}(X)) \cap f\]Similarly, the closing by reconstruction reconstructs the background instead of the foreground.
- Parameters:
f – Input image 𝑓
markers – Marker image (must have the same value type of 𝑓)
nbh – Elementary structuring element.
- Returns:
An image whose type is deduced from the input image
- Precondition:
\(markers \le f\) (for (3) \(markers \ge f\))
- Exception:
N/A
Notes
Complexity
Example 1 : Staff lines reconstruction

Original image |
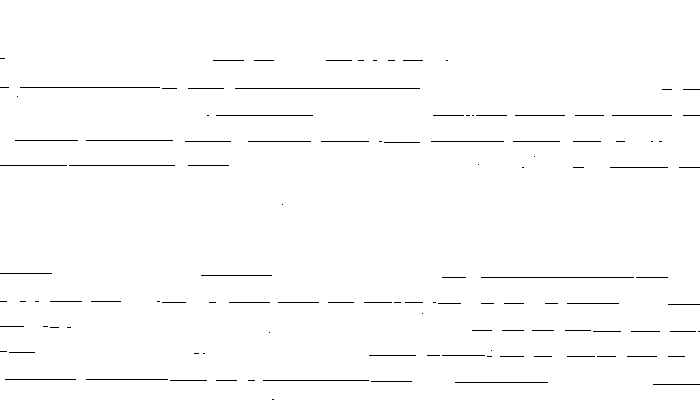
Markers obtained by the Hit or Miss transform. |
Given an original image and some markers obtained with the Hit or Miss transform. The geodesic reconstruction (with the 4-connection) of the original image by the markers give the objects touching staff lines. All objects that do not touch the staff lines are removed.
auto markers_ = markers1 or markers2;
auto all_touching = mln::morpho::opening_by_reconstruction(input, markers_, mln::c4);
mln::io::imsave(not all_touching, argv[5]);

Geodesic reconstruction from the markers.
If we want to reconstruct only the staff line only, use an horizontal SE x-o-x.
auto lines_only = mln::morpho::opening_by_reconstruction(input, markers_, mln::c2_h);
mln::io::imsave(not lines_only, argv[6]);

Horizontal reconstruction from the markers.
Example 2 : Dense region reconstruction

a. Original image |

b. Markers from the Rank filter |

c. Dilated of the original image a |
// Make blobs connected
auto disc = mln::se::disc(4);
auto dil = mln::morpho::dilation(input, disc);
// Get markers for large connected components
auto rect = mln::se::rect2d(20, 20);
auto markers = mln::morpho::rank_filter<std::ratio<1,4>>(input, rect, mln::extension::bm::fill(false));
// Reconstruction of the large CC
auto rec = mln::morpho::opening_by_reconstruction(dil, markers, mln::c8);
Given an original image. We first start with a Rank filter to locate dense region (regions with much more foreground pixels that background pixels) that gives us markers. Then a dilation with a small disc allows to connect objects. The reconstruction of the dilated image with a the markers gives a mask for the dense region. Finally, we just have to mask the input with the mask to get the objects in dense regions:
auto out = mln::clone(rec && input);

d. Reconstruction of c from the markers b |

Input (a) restricted to the mask (d) |